Fig. 1
Download original image
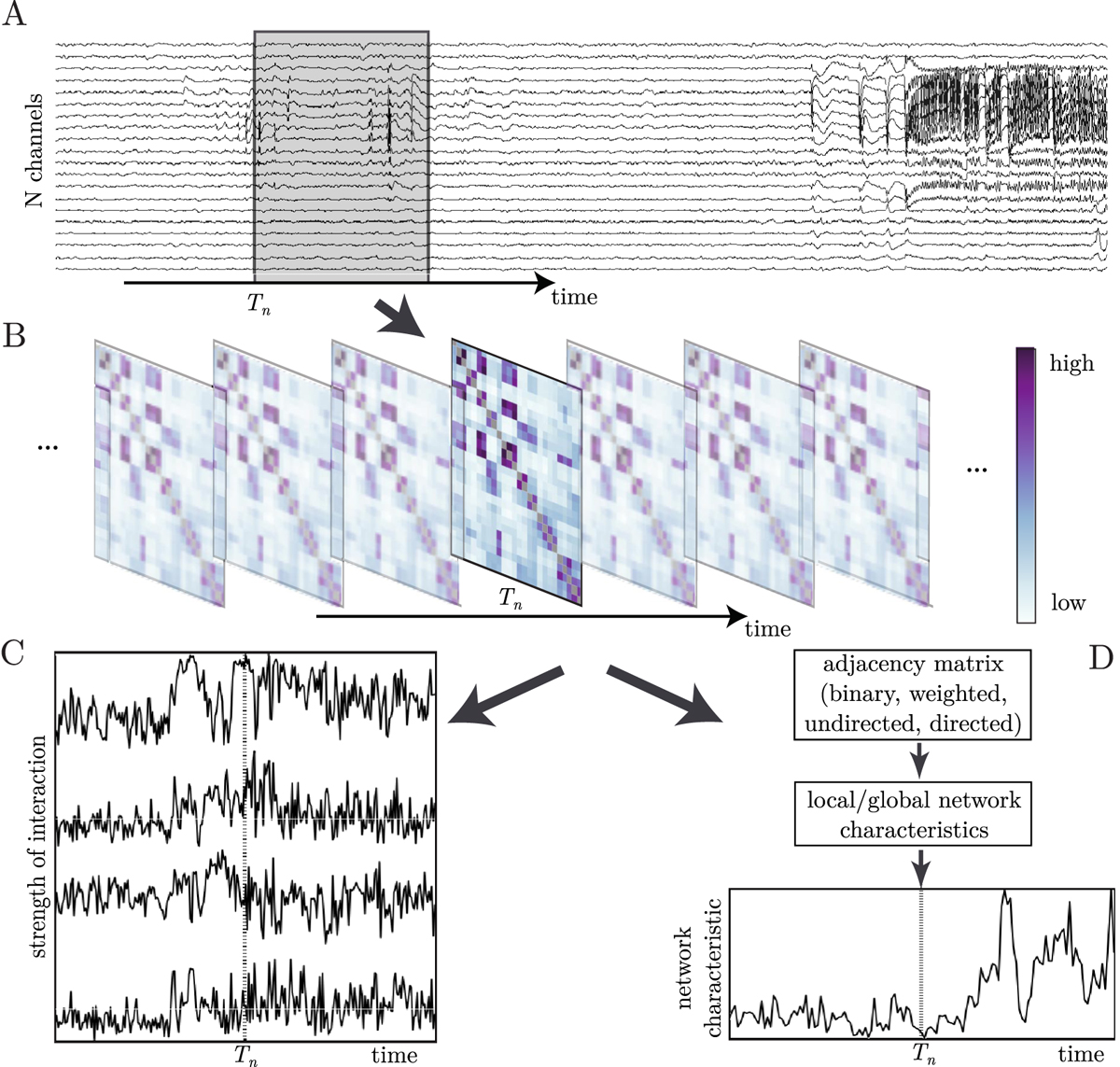
Schematic of interaction-analysis-based approaches to characterize time-varying brain dynamics. (A) Sliding-window analysis: long-lasting multichannel recordings of brain dynamics (here: intracranial EEG) are segmented into successive (non)overlapping windows; Tn denotes the time point associated with the left boundary of the nth window (marked in gray). (B) Time-dependent sequence of interaction matrices: each matrix contains estimates of an interaction property (strength or direction) calculated from the brain dynamics within a given window for all pairs of N sampled brain regions. (C) A bivariate analysis approach renders a time-dependent sequence of an interaction property (here: strength of interaction) for each pair of sampled brain regions (upper three sequences are shifted upwards to enhance readability). (D) A network analysis approach renders a time-dependent sequence of a local or global network characteristic. Time-dependent sequences depicted in (C) and (D) are then subject to further analyses.

